

Elaborative rehearsal leads to much stronger long-term memory storage, making it easier to remember. Semantic encoding refers to the general meaning of an event. Visual encoding and acoustic encoding are self-explanatory they are named for the sensory modality through which they operate. If I tried to connect the information to something meaningful in my life, I would be practicing elaborative rehearsal, which is a much more effective studying method. Encoding may be visual, acoustic, or semantic. While the information is stored in me short-term memory, I have not really understood the information. When I study for exams, I usually make flashcards and go over them again and again until I feel I have memorized the information. Maintenance rehearsal is a common way of studying because it is so easy to use. There is a possibility that this information will eventually get stored in long-term memory, but it is unlikely. This method involved repeating information over and over again to keep it in the short-term memory. Many students, including myself, practice maintenance rehearsal. One of the hardest things about being a college student is trying to find a good study method. Without encoding, information would never get stored in the short-term or working memory. I think the encoding process is the most important step because this is only way information is stored in the memory. We can bring information from the storage area of the flash drive onto the monitor where we are able to see it again. This action is similar to a monitor of a computer. Finally, the information must be able to be recalled or retrieved.
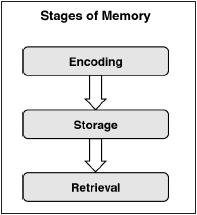
Next, the information must be stored somewhere, like on a floppy disk or flash drive. Encoding can be compared to a keyboard the information has to first be inputted before it can be stored. The first step is encoding the information, or getting it into the memory system. The memorization process can be compared to the different parts of a computer. College students have to rely on studying to be able to store and then recall the information. Unfortunately, photographic memories are not very common. I would be able to look at something one time and remember it perfectly. Suggest recall is probably more accurate than Bartlett suggested.There have been many times throughout my college career when I wished I had a photographic memory. Another study found that recall was much more accurate when participants were told from the outset that recall was important (Gauld & Stephenson 1967) The participants were not given very specific instructions at the outset about what they should do. One weakness is that the study was conducted rather casually with no set standards about where and how people recalled the information. Study may tell us very little about everyday memory. In such cases our memories are not affected by cultural experiences and therefore we may recall things quite accurately. Most of the time we use memory to deal with everyday experiences. Means we cannot fully trust the resources of the study as he may have misinterpreted results.Īnother weakness is that the story is unusual and therefore may not reflect everyday memory processes.

To see how visual encoding works, read over this list of words: car, level, dog, truth, book, value. Since Bartlett had the belief that recall would have been affected by Cultural Expectations he may have been more likely to have seen Visual encoding is the encoding of images, and acoustic encoding is the encoding of sounds, words in particular. The conclusions depend on how you interpret the results.

One weakness is that Bartletts own beliefs were likely to have affected the way he interpreted data.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
